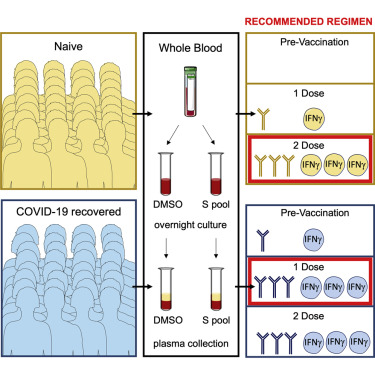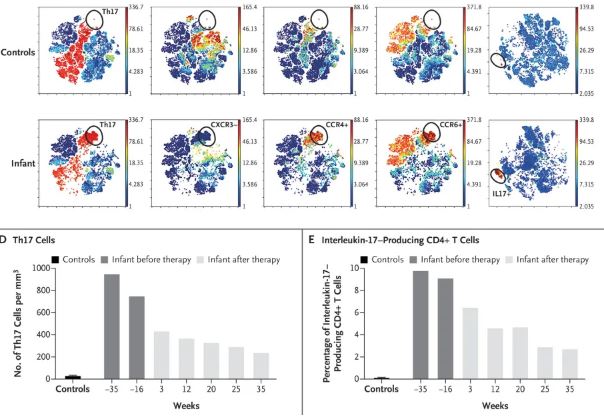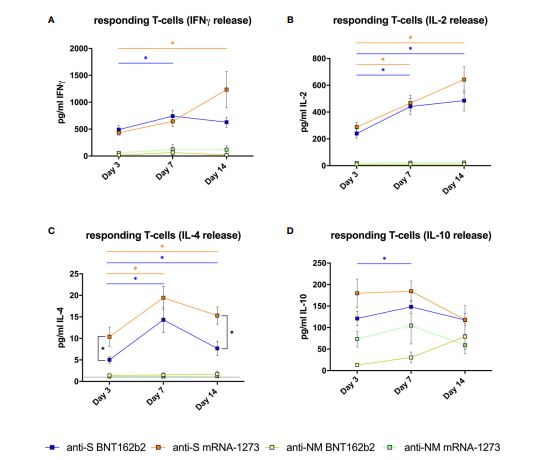
Induction of High Levels of Specific Humoral and Cellular Responses to SARS-CoV-2 After the Administration of Covid-19 mRNA Vaccines Requires Several Days.
Sergio Gil-Manso, Diego Carbonell, Luis López-Fernández, Iria Miguens, Roberto Alonso, Ismael Buño, Patricia Muñoz, Jordi Ochando, Marjorie Pion and Rafael Correa-Rocha.
October 2021. ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.726960
This refractory period in the induction of specific immunity observed after completing the vaccination could constitute a window of higher infection risk, which could explain some emerging cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection in vaccinated people.